For Students
For Students
Bachelor Courses
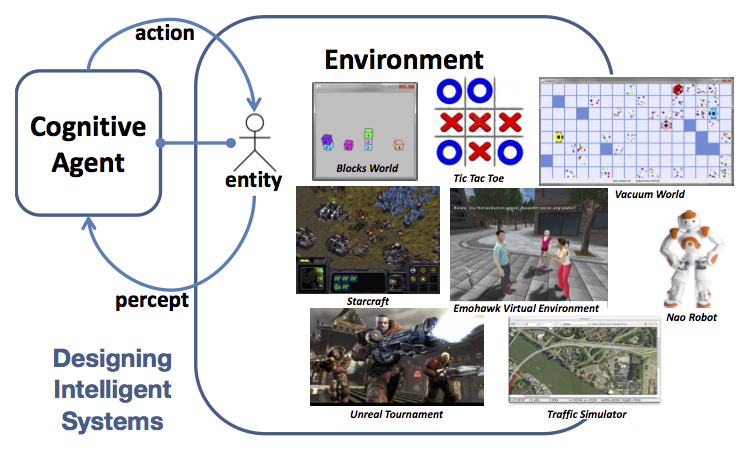 |
TI1906 - Logic Based AI AI (Artificial Intelligence) techniques that are discussed in this course are knowledge representation and reasoning techniques, and multi-agent technology. Students are taught how to develop a multi-agent system that uses knowledge representation to reason about the environment in which the multi-agent system operates. In the Project Multi-agent systems following this course, students develop, based on the knowledge gained in this course, a team of intelligent agents that drive bots in the game Unreal Tournament. |
 |
TI1606 - Project Multi-Agent Systemen Door middel van dit project leren studenten de concepten en technieken die zij in het college Logic-Based Artificial Intelligence hebben geleerd in de praktijk toe te passen. De student is na afloop in staat projectopdrachten in teamverband te analyseren, agenttechnologische oplossingen te selecteren, te specificeren, te implementeren, en te testen. In het project programmeren studenten een team van agents die bots aansturen in de game Unreal Tournament. Strategieën moeten worden ontwikkeld voor een capture the flag scenario, waarin bots als team zo vaak mogelijk de vlag van de tegenstander moeten pakken. Aan het eind van het project vindt een competitie plaats waarin de teams van de verschillende groepen tegen elkaar strijden om de hoofdprijs. |
 |
TI2736A - Computational Intelligence Dit vak geeft een introductie in een aantal technieken uit de kunstmatige intelligentie. De nadruk ligt daarbij op zelflerende en zelforganiserende systemen. We beginnen met de vraag 'wat is (kunstmatige) intelligentie?' en beantwoorden deze vraag vervolgens aan hand van een aantal metaforen:
|
Master Courses
 |
IN4010 - Artificial Intelligence Techniques Artificial Intelligence techniques for building cognitive agents and decision support systems are presented. Various techniques needed are discussed, including automated reasoning, action selection and planning, and learning. In addition, various models needed to design and build such systems are discussed, including cognitive architectures, mental models, decision making, and strategic interaction. |
 |
IN4179 - Intelligent User Experience Engineering Living, work, training and travel environments contain more and more networked information and communication technology, e.g. in homes, offices, serious games and cars. A major challenge is to realize fine user experiences for the persons interacting with this technology. These user experiences concern both the traditional usability aspects —such as the effectiveness and efficiency of task performances, and user satisfaction— and the new user aspects of acting in a smart environment—such as trust and emotion. For the Intelligent User Experience Engineering (IUXE) course (Masters), we choose to provide a coherent cognitive engineering framework for design and evaluation of human-machine collaboration. Based on this framework, we will elaborate on current theories, methods, technologies and best practices for establishing advanced (intelligent) user interfaces and for interactions with complex information and communication systems. |
 |
IN4354 - Seminar Human-Agent/Robot Teamwork In this course, we study intelligent systems that cooperate with humans to achieve a common objective. These systems can consist of intelligent software agents, but may also be embodied in the form of robots. The theme of this course is thus human-agent/robot teamwork (HART). More specifically, the focus is on three main areas within HART: - organizational modeling languages: languages for modeling an organization of agents and/or humans by specifying the roles that can be played, the norms that should be followed, etc. - socio-cognitive robotics: the study of social robots that are expected to become part of our daily lives, such as serving robots in our homes, robots that assist in challenging tasks such as surveillance or crisis rescue operations, care-taking assistants for the elderly, etc. - explainable AI (XAI): the study of how to explain to human users or teammates why certain decisions were taken by agents or robots and what line of reasoning was followed to come to this decision. |
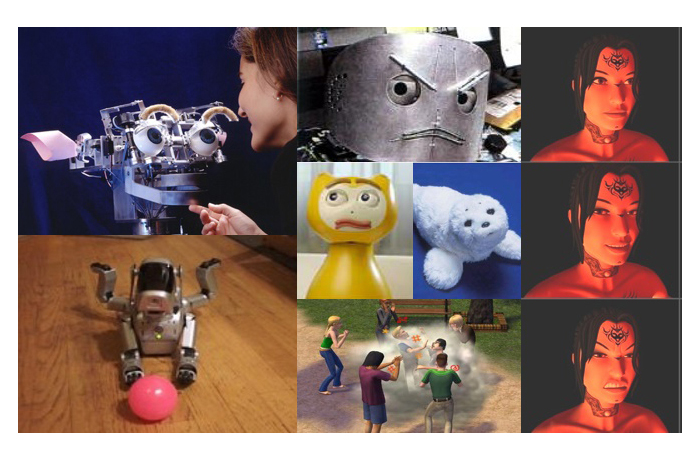 |
IN4188 - Seminar Affective Computing Companion Robots, the virtual inhabitants of the computer game The Sims, but also smart cameras with Smile Shutter technology are systems that have been designed to interact with humans in a natural way. One way to achieve this, is to use digital emotion technology, for example a Computational Model that simulates artificial emotions for the characters in the The Sims. The field of computing with emotion is called Affective Computing. Even simple emotions of The Sims are based upon a theory of emotion. In this course you will learn to recognize different psychological views on emotion, as well as how and why these views are used in affective computing. We will discuss several existing models and learn about emotion recognition, emotion simulation and emotion expression by robots and agents. You will yourself develop a system that makes use of Affective Computing techniques. Overall, this course will give you insights into the fun (gaming, robots) and glory (theoretical predictions, enhanced HCI) of affective computing. |
 |
IN4304 - Empirical Research Methods - (weblectures) The main topics of study considered in light of the above learning outcomes are:
|
 |
CS4015 - Behaviour change support systems - (weblectures) Behavior change support systems (BCCS) are computer-based systems that support individuals to form, alter or reinforce cognitions, attitudes or behaviors without using coercion or deception. They can serve individuals throughout the various stages of a change process, such as awareness developing, contemplation, action strategy development, development of new behaviors, and maintaining these new behaviors. Virtual healthcare coaches, negotiation support systems, and applications that provide individuals with personalize financial guidance are three examples of these systems. To establish, modify or maintain change BCCS can deploy computerized persuasive strategies (e.g. reducing effort to establish target behavior, or argumentation and reflection strategies), simulations (e.g. serious gaming, virtual reality), relational software agents (e.g. ePartners, virtual coaches), and personalization based on longitudinal user data. BCCS are found in many domains, including education, sales, negotiation, management, and particular in the health domain. |
