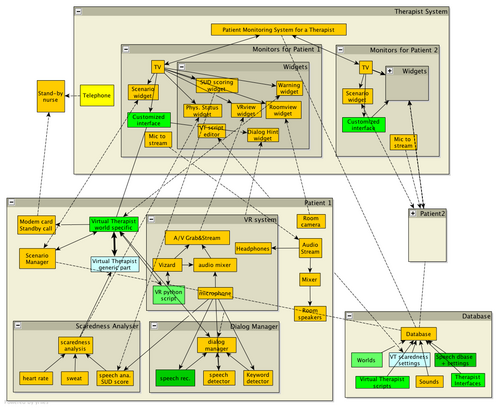
VRET Archi
The goal of the system architecture is to provide an infrastructure for VRET related projects so that we
- provide the therapist with basic feedback like video, sound, heart rate
- provide programmers with a common approach and tools to handle remote therapy
- enable re-use of commonly required components
- easy switching between various therapies
The figure below shows the first proposal we arrived at after meeting with Willem-Paul, Niels, Christian, Guntur, and Daniel.
Hardware
Check VRET_Hardware for details on the VR machine
Check Video_Hardware for details on the video streaming hardware
Network Mechanism
To handle communication between the patient monitoring system and the patient computers, we currently use plain sockets. While fast and simple, this requires all firewalls on the route between server and client to be open. Usually these ports will not be open except inside a single domain. Opening them will require negotiations with the network security staff and seems better avoided if possible.
I discussed this issue with Ruud, Tim Verwaart, and a number of people in the computer graphics group. Our safest bet seems to be using the HTTP ports instead of just arbitrary sockets.
We have the following requirements for the connection
- server (the side handling the call) needs to be notified when the network connection gets disabled.
- some people in the project asked if it's possible to call functions directly instead of building large
if(received="commandX") then ....loops. RPC would enable somethign like that. That will mostly replace the if-then constructs with "def commandX()" constructs so I do not belief that it will save much space. - Support for "channel coding": putting objects into the stream and re-building an object out of it at the other end of the channel. In Java this is trivial by extending "serializable" but in Python apparently it is not. An XML library is just one of many solutions for that. XML blows up data easily by a factor 6 and requires extra parsing causing an order of magnitude slowdown [ File:Xmlrpc-perf.pdf ]). For small transactions there is not much difference and in our case XML seems acceptable as transfer format.
- Many python RPC servers on a single computer have to be able to use the same port at the same time. So the addressing seems to require more than just the computer name and port number.
One possibility is xml-rpc. A number of people in the graphics group working often with this do recommend xml-rpc. Maybe it's possible to replace the serve_forever() call with something else?